magazine_ Article
The consequences of a winter with little snow are felt in summer
New web application monitors water supplies stored in the form of snow throughout the Alps
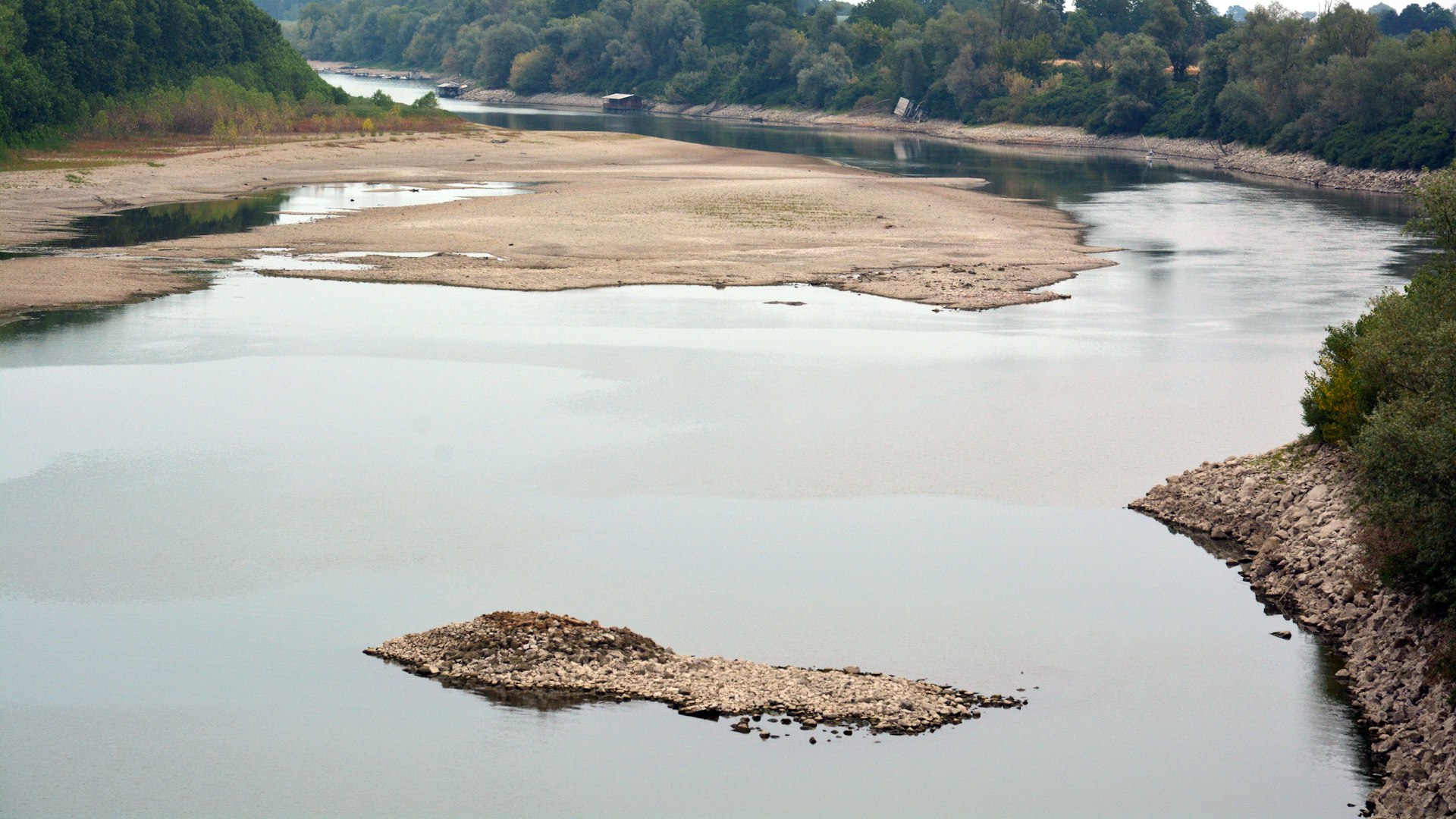
The consequences of a dry and warm winter such as that of last year, are felt the following summer when those who need water must share increasingly scarce resources. The river Po in Piacenza (Italy), June 2022.
Credit: Pierlino Bergonzi | All rights reserved
A team of researchers and entrepreneurs from MobyGIS, Eurac Research, and Sinergise, were funded by the European Space Agency to create the first service that monitors water reserves stored in the snow in the entire Alpine range and provides high-resolution real-time maps. The prototype can be tested free of charge for the next six months before it becomes commercialized.
The web service is called eo4Alps and has an intuitive interface: a large part of the screen is taken up by maps, with a tool in the side bar to navigate the maps and select the parameters you want to visualize. Users can select the area of the Alps they are interested in and choose their preferred parameters: the extent of the snow cover, snow depth, and its water equivalent - to see how much water will be available once the snow has melted. Given that in Europe most of the winter precipitation above 1,000 meters comes in the form of snow which enters the hydrological cycle after melting, calculating this reserve is crucial - especially now that the climate crisis is steadily thinning resources. "There are already a hundred stakeholders interested in our application - hydroelectric power plant operators, regional environmental agencies, private companies that provide weather forecasts or develop sensors, and of course environmental research and monitoring centers," announces Matteo Dall'Amico, CEO of MobyGIS, the company leading the project.
 Credit: eo4alps snow consortium | All rights reserved
Credit: eo4alps snow consortium | All rights reservedUntil now, some monitoring tools have existed, but they were limited to single regions or had low resolution; eo4Alps spans the entire Alps and offers data resolution equal to 250 meters. "We merged the advantages of physical models with those of remote sensing to be able to make more precise estimates," explains Mattia Callegari, researcher at Eurac Research's Institute for Earth Observation. "We used both optical images from Sentinel-2 and Sentinel-3 satellites and radar images from Sentinel-1. Computer science colleagues of Sinergise then packaged the infrastructure for data processing and the web platform."
The prototype, recently presented to the scientific community, will be accessible for free for about six months. At the end of the project, the web service will be turned into a commercial product. In fact, the project is part of a European Space Agency funding program that specifically aims to promote active, market-oriented collaborations between research centers and business enterprises.
Access the pilot version of the web application (“demonstrator”): https://www.waterjade.com/eo4alps-snow